Building the Future with IoT Smart Building Solutions
Traditional building management systems often result in high maintenance costs, inefficient operations, and unnecessary energy consumption. Smart buildings, on the other hand, uses advanced technologies to connect, collect, and analyze data to automatically and remotely control building operations.
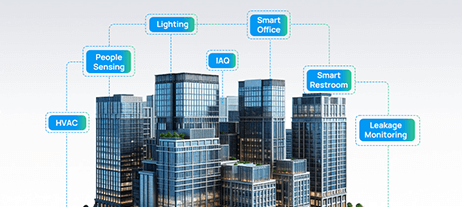
In smart buildings, IoT solutions, including sensors, controllers, and gateways, enable real-time monitoring and automation to improve efficiency, comfort, and safety. Milesight delivers comprehensive wireless IoT solutions for smart buildings, enabling real-time people sensing, optimized resource allocation, and efficient facility management, unlocking new levels of building intelligence.
Insightful Industry Reports to Guide Your Smart Building Strategy Worldwide

Frost Radar: Top IoT Innovators in
Smart Building Sensors, 2025

Policy-Driven Development
of Smart Buildings
in Europe